Three major changes over the past decade have created a need for manufacturers to change their procurement systems.
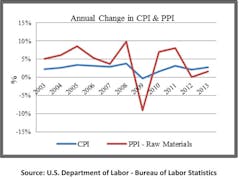
First, raw material and energy costs have increased 55% since 2002, while the Consumer Price Index (CPI) has increased less than 31%. Producer price increases, meanwhile, have outpaced consumer prices by more than 76% over the past 10 years, squeezing the margins of most manufacturers (see chart below).
Second, during the same period the volatility of commodity prices, which make up a large portion of raw material and energy costs, has doubled. Effective management of raw material price volatility is essential for success at most manufacturers (see chart below).
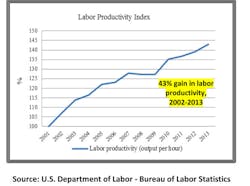
Finally, 43% gains in labor productivity since 2002 have drastically reduced labor cost as a percentage of total costs, leaving raw material and energy costs a much larger component of most company’s cost structure. This third component intensifies the first two changes, making their impact on price risk even more significant (see chart below).
The bottom line: Productivity gains made by manufacturers over the past 11 years have been offset by higher raw material and energy costs, while profits are much more volatile due to greater swings in input costs.
In today’s world of more expensive and more volatile raw material and energy prices, businesses with exposure to commodity inputs must radically change their procurement model to merge buying and selling systems, develop the best hedging options and manage the gross margin in addition to costs.
Three areas must be developed for manufacturers to thrive in today’s environment:
- price risk incorporated into a company’s risk management system;
- hedging strategies adopted and tools created to manage price risk (a hedge is an action that protects against adverse price movements);
- a margin management system created that links buying and selling.
Risk Management
Risk management systems should address how to manage price volatile raw material and energy inputs with sales prices that are difficult to increase. Analyzing price risk, defining price risk tolerance and developing a system to manage the risk within the established tolerance are essential to prudent operations at manufacturing and distribution companies.
Exposure or position reporting is also an essential building block to a risk system. Position reports link the units of input bought with the units of output sold. Net exposure—your “long or short” position—is where your price risk lies. Understanding the cost drivers of your inputs and their price volatility will help you establish position limits that adhere to the company’s risk tolerance.
Exposure management and quantifying risk tolerance are the foundation for the other two areas essential in changing the procurement model: hedging and margin management.
Hedging
Hedging strategies based on the company’s risk tolerance define what tools are appropriate to hedge your price risk. This risk can be held internally or passed on to customers, vendors and third parties. Key items to consider while developing hedging tools include administrative complexity, staffing requirements, capital needs and industry sophistication. Hedging tools can be simple, like escalators in a sales contract or minimum/maximum quantities on supply contracts, to very complex options strategies or over-the-counter instruments tailored to very specific risk.
Analyzing your price risk hedging options will provide unique insight into your business. If a risk is difficult or expensive to hedge, your focus needs to turn to eliminating units of exposure to that risk.
A tangible benefit to developing an exposure system, risk parameters, hedging strategies and tools is you will improve your procurement skills and buy better, even if you forget to create and implement a margin management system.
Margin
Margin management systems link the position and price risk for a company’s inputs and outputs. It includes exposure reporting, earnings forecasts and scenario planning. Margin management uses risk management systems and hedging strategies to protect and enhance margins while connecting the procurement, production and sales functions of the company.
Warning signs to help identify your risk and margin management systems that need to be revamped include:
- Your organization spends more time managing costs than margins.
- Your organization does not have a method to measure raw material and energy price risk.
- Sales decisions are made independent of buying decisions and vice versa.
- “Higher raw material and energy costs” frequently explain away earnings shortfalls.
- Your organization has a separate department called procurement or purchasing.
- “Risk management” mainly refers to the relationship you have with your insurance broker.
- “Hedging” conjures up the image of expensive, complex transactions that are to be avoided.
To compete in a global economy, manufacturers must adapt their procurement systems to today’s environment.
Steve Rosvold has run KRM Business Solutions for the past eight years. KRM provides interim CFO services to middle-market companies, and business education and financial intelligence to the business community. Rosvold previously spent 22 years in finance and strategic planning at Cargill Inc. and ConAgra Foods.