Inventory Accuracy Improves Performance on Logistics Metrics
Inventory accuracy is the variance between perpetual inventory and physical inventory. It is an important part of supply chain management because organizations that allow their inventory accuracy to drop run several risks. Misleading inventory levels may make it seem that these organizations have more inventory than they actually do, which leads the organizations to sell stock that is not there and can result in dissatisfied customers. Inaccurate inventory data may also mask inventory that is actually there, which can lead to stock remaining in a warehouse until it becomes obsolete.
A related issue is increased inventory carrying cost. To get a better idea of how much additional cost can be related to carrying inventory, APQC reviewed data from its Open Standards Benchmarking in logistics. The data shows a nearly 11 percent difference between top performing and bottom performing organizations regarding inventory value as a percentage of revenue:
- 16.0% -- Bottom performers
- 9.4% -- Median
- 5.2% -- Top performers
For an organization with $5 billion in revenue, this difference translates into $540 million in inventory carrying cost.
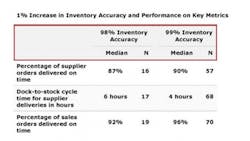
Aside from lower inventory carrying cost and more satisfied customers, higher inventory accuracy can lead to improved performance in other logistics processes. APQCs Open Standards Benchmarking database indicates that an increase in inventory accuracy from 98 percent to 99 percent is associated with an increase in supplier orders delivered on time, faster dock-to-stock cycle time, and an increase in the amount of sales orders delivered on time (Table 1).
Improvements in the metrics listed in Table 1 can affect the entire supply chain. When inbound deliveries to an organization arrive within the scheduled time frame and are quickly moved into the warehouse, those materials are available for customer orders sooner. Faster processing and delivery of products leads to satisfied customers and lower inventory carrying cost.Getting That One Percent
So how does an organization obtain a one percent (or more) improvement in inventory accuracy? The key to inventory accuracy is creating visibility.
Organizations can use radio frequency identification (RFID) tags to track inventory in the warehouse in real time. The data provided by these tags can be maintained in a warehouse management system that is integrated with the organizations order management system to ensure that employees processing customer orders have accurate product availability information.
Organizations can also work with suppliers and carriers to obtain real-time data on inbound deliveries so that the organization can accurately note in the systems when materials arrive and are available. Perhaps most importantly, organizations can improve inventory accuracy by taking steps to identify and correct defective processes within their logistics functions that generate inventory errors.
To ensure that inventory accuracy efforts are working, organizations must make a concerted effort to track performance metrics such as the ones discussed in this article. This allows organizations to determine whether they should revisit their inventory accuracy strategy to see if any adjustments are needed. Monitoring performance also enables organizations to benchmark themselves against other companies to determine if further improvement is needed.
APQC's research shows that inventory accuracy can do much more than just reduce inventory carrying cost and reduce stock outages. Efforts to improve inventory visibility can affect many logistics processes, from the receipt of inbound materials to order processing. Although these efforts may require investments in new systems and data monitoring, they can ultimately have a positive result on business.
APQC is a member-based nonprofit and a proponent of benchmarking and best practice business research. Working with more than 500 organizations worldwide in all industries, APQC focuses on providing organizations with the information they need to work smarter, faster and with confidence.