Nearsourcing, Low-Cost Natural Gas Drive Chemical Industry Growth
The chemical industry presents an interesting U.S. success story. It was only a few years ago that many predicted the demise of the chemical industry in the United States, as the power of China and Dubai seemed unstoppable.
The good news is that this industry is rebounding along with the rest of the United States, and that reports of its death were premature.
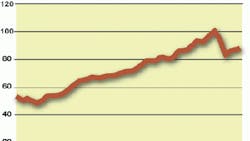
The chart below clearly shows that we have not regained the early-2008 production apex; production is currently tracking at September 2004 levels. However, the future for this industry looks bright for several reasons.
First, nearsourcing in the United States in many industries (including the automotive industry) bodes well for continued demand for goods made in the chemical industry. We are projecting a strong demand pull on chemical producers through the next five years, with the exception of a mild downturn in 2014.
Second, U.S. chemical producers should be able to enjoy a long-term feedstock cost advantage thanks to low-cost natural gas. The great shale finds in the United States ensure a steady supply of natural gas for decades to come. Fracking should be allowed to continue, owing to the great advantages it affords in terms of supply and cost savings to this nation. Environmentalists who are unhappy over the use of water in this process may be assuaged if the industry switches to readily available nitrogen. The use of nitrogen will push costs up, but not enough to undo the cost benefit of domestic gas.
Domestic demand and a competitive cost structure suggest that industry leaders should plan to invest in domestic operations in the near term in order to secure the production capabilities that will be demanded in the year to come. Now is the time to invest in infrastructure, manufacturing process, R&D and new-customer development.
Economics in the News
An aggressive move by Iran or against Iran is likely to cause the price of oil to spike, but a spike does not cause long- or medium-term economic disruption. There would have to be a sustained disruption of a significant source of oil in order for the United States and the global economy to slip back into recession. Should Iran sustain damage to its oil fields or pipelines, this would cause prices to spike. However, the effect would likely be short term, as other producers would ramp up production to meet the demand. Saudi Arabia and others hate high oil prices, as it invariably results in animosity toward oil-producing nations and an increased desire for alternative forms of energy. These are two things oil-producing nations cannot afford.
I cannot predict whether Iran will attack or be attacked, but I am confident we will not see significantly sustained higher oil prices in 2012.
Contributing Editor Alan Beaulieu is an economist and president of the Institute for Trend Research.